The History of Printing
The Evolution of Printing: From Gutenberg to 3D Printing
Printing has been an essential tool for communication, education, and innovation throughout history. From the groundbreaking invention of Johannes Gutenberg's printing press in the 15th century to the revolutionary advancements in 3D printing technology today, the evolution of printing has been a testament to human ingenuity and creativity. In this article, we will explore the fascinating journey of printing from its humble beginnings to its modern-day applications.
The Gutenberg Revolution:
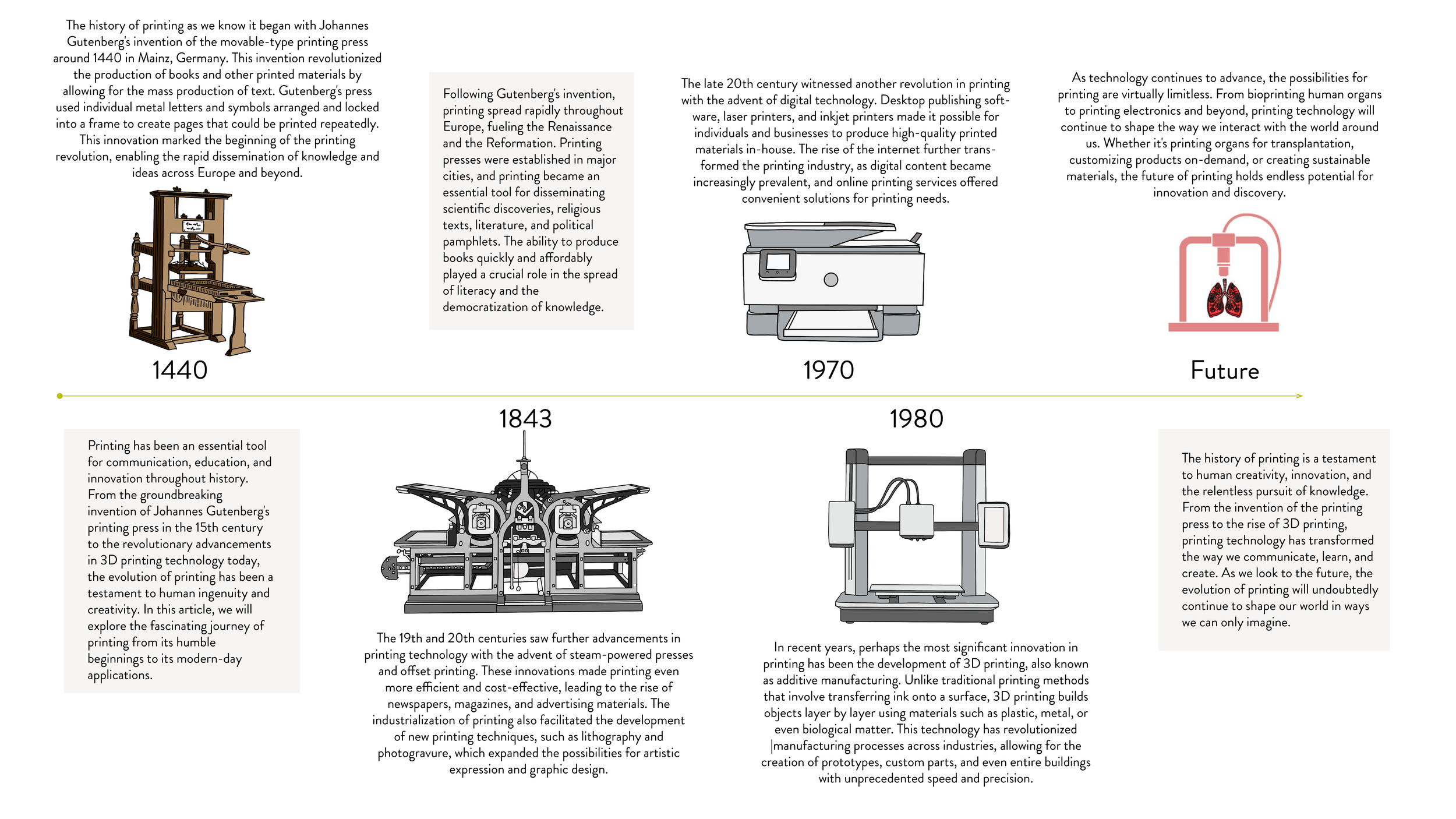
The history of printing as we know it began with Johannes Gutenberg's invention of the movable-type printing press around 1440 in Mainz, Germany. This invention revolutionized the production of books and other printed materials by allowing for the mass production of text. Gutenberg's press used individual metal letters and symbols arranged and locked into a frame to create pages that could be printed repeatedly. This innovation marked the beginning of the printing revolution, enabling the rapid dissemination of knowledge and ideas across Europe and beyond.
The Spread of Printing:
Following Gutenberg's invention, printing spread rapidly throughout Europe, fueling the Renaissance and the Reformation. Printing presses were established in major cities, and printing became an essential tool for disseminating scientific discoveries, religious texts, literature, and political pamphlets. The ability to produce books quickly and affordably played a crucial role in the spread of literacy and the democratization of knowledge.
Industrialization and Modern Printing:
The 19th and 20th centuries saw further advancements in printing technology with the advent of steam-powered presses and offset printing. These innovations made printing even more efficient and cost-effective, leading to the rise of newspapers, magazines, and advertising materials. The industrialization of printing also facilitated the development of new printing techniques, such as lithography and photogravure, which expanded the possibilities for artistic expression and graphic design.
Digital Printing and the Internet Age:
The late 20th century witnessed another revolution in printing with the advent of digital technology. Desktop publishing software, laser printers, and inkjet printers made it possible for individuals and businesses to produce high-quality printed materials in-house. The rise of the internet further transformed the printing industry, as digital content became increasingly prevalent, and online printing services offered convenient solutions for printing needs.
The Rise of 3D Printing:
In recent years, perhaps the most significant innovation in printing has been the development of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing. Unlike traditional printing methods that involve transferring ink onto a surface, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer using materials such as plastic, metal, or even biological matter. This technology has revolutionized manufacturing processes across industries, allowing for the creation of prototypes, custom parts, and even entire buildings with unprecedented speed and precision.
The Future of Printing:
As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for printing are virtually limitless. From bioprinting human organs to printing electronics and beyond, printing technology will continue to shape the way we interact with the world around us. Whether it's printing organs for transplantation, customizing products on-demand, or creating sustainable materials, the future of printing holds endless potential for innovation and discovery.
Conclusion:
The history of printing is a testament to human creativity, innovation, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. From the invention of the printing press to the rise of 3D printing, printing technology has transformed the way we communicate, learn, and create. As we look to the future, the evolution of printing will undoubtedly continue to shape our world in ways we can only imagine.
Works Cited
“Gutenberg Press.” International Printing Museum, https://www.printmuseum.org/gutenberg-press. Accessed 21 Feb. 2024.
Jones, Neil. Digital Printing: A Brief History -. 28 Sept. 2022, https://cdp.co.uk/news/digital-printing-a-brief-history/.
“Koenig and Bauer’s Steam Powered Printing Press.” Age of Revolution, https://ageofrevolution.org/200-object/koenigs-steam-powered-printing-press/. Accessed 21 Feb. 2024.
Panja, Nabanita, et al. “3D Bioprinting of Human Hollow Organs.” AAPS PharmSciTech, vol. 23, no. 5, May 2022, p. 139. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02279-9.
The Printing Revolution | Western Civilization. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/atd-herkimer-westerncivilization/chapter/the-printing-revolution/#:~:text=The%20printing%20press%20spread%20within,more%20than%2020%20million%20volumes. Accessed 21 Feb. 2024.